AutoFS allows to automatically mount network shares on demand. Compared with traditional fstab configurations, using AutoFS has the following benefits.
Nfs Mount Fstab Example
With the hard option (default one), the boot process will pause if there is a problem mounting the nfs share and repeated tries are made to mount the share indefinitely. If the soft option is used, then the mount fails after retrans retransmissions have been sent. On the other hand, autofs only mounts nfs shares when they are needed and accessed.
- Beyond mounting a file system via NFS on a remote host, other options can be specified at the time of the mount to make it easier to use. These options can be used with manual mount commands, /etc/fstab settings, and autofs. The following are options commonly used for NFS mounts.
- When we try access the mount point then autofs service will mount nfs share automatically. Steps to mount NFS share using autofs in Ubuntu Linux. Step:1 Install the autofs package using apt-get command. email protected:$ sudo apt-get install autofs.
- With AutoFS, directories are automatically mounted when they are accessed and are unmounted after a period of inactivity — can reduce boot time and improve overall performance.
- Auto-mounting via
fstabwill fail if the network connection to the network share is not yet established during boot time (common issue with WiFi netwoks) — not an issue with AutoFS, as the shares are mounted on demand.
However, mounting a NFS directory using AutoFS requires a little more work, compared to adding a rule to the /etc/fstab file, here is an example.
Install dependencies:
Create a mount point:
Configure the mount point, add the following line to the end of the file /etc/auto.master:
Note: That line tells the AutoFS service that the mount points under /nfs are configured in file /etc/auto.nfs.
Add the following line to the file /etc/auto.nfs (create the file if it does not exist and adopt the hostname of the NAS and the name of the NFS directory):
Note: In the example above, the NFS share is mounted read-only, with some flags to optimize performance. Adopt the NFS mounting options to your needs, if necessary.
Restart the AutoFS service:
External Links
You need to configure autofs manually by editing its configuration files with a text editor, such as vim. There are two basic steps to configure autofs—the master map file, and specific map files. Buy autotune for mac.
The default master configuration file for autofs is /etc/auto.master. You can change its location by changing the value of the DEFAULT_MASTER_MAP_NAME option in /etc/sysconfig/autofs. Here is the content of the default one for SUSE Linux Enterprise Server:
The |
Although commented out (#) by default, this is an example of a simple automounter mapping syntax. |
In case you need to split the master map into several files, uncomment the line, and put the mappings (suffixed with |
|
Entries in auto.master have three fields with the following syntax:
The base location where to mount the autofs file system, such as /home.
The name of a map source to use for mounting. For the syntax of the maps files, see Section 30.2.2, 'Map Files'.
These options (if specified) will apply as defaults to all entries in the given map.
Tip: For More InformationKingdom come deliverance lost sword. For more detailed information on the specific values of the optional map-type, format, and options, see the auto.master manual page (man 5 auto.master).
The following entry in auto.master tells autofs to look in /etc/auto.smb, and create mount points in the /smb Turbomosaic 3 0 6 – photo mosaic maker tutorial. directory.
Direct mounts create a mount point at the path specified inside the relevant map file. Instead of specifying the mount point in auto.master, replace the mount point field with /-. For example, the following line tells autofs to create a mount point at the place specified in auto.smb:
If the map file is not specified with its full local or network path, it is located using the Name Service Switch (NSS) configuration:
Important: Other Types of Maps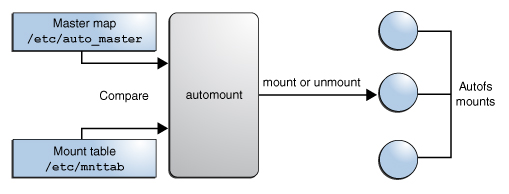
Although files are the most common types of maps for auto-mounting with autofs, there are other types as well. Fontxchange 5 3. A map specification can be the output of a command, or a result of a query in LDAP or database. For more detailed information on map types, see the manual page man 5 auto.master.
Autofs Mount Options
Map files specify the (local or network) source location, and the mount point where to mount the source locally. The general format of maps is similar to the master map. The difference is that the options appear between the mount point and the location instead of at the end of the entry:
Make sure that map files are not marked as executable. You can remove the executable bits by executing chmod -x MAP_FILE. Quarkxpress 13 2 1 – desktop publishing solutions.
Specifies where to mount the source location. This can be either a single directory name (so-called indirect mount) to be added to the base mount point specified in auto.master, or the full path of the mount point (direct mount, see Section 30.2.1.1, 'Direct Mounts').
Nfs Mount Fstab
Specifies optional comma-separated list of mount options for the relevant entries. If auto.master contains options for this map file as well, theses are appended.
Centos Mount Nfs Autofs
Nfs Mount Fsid
Specifies from where the file system is to be mounted. It is usually an NFS or SMB volume in the usual notation host_name:path_name. If the file system to be mounted begins with a '/' (such as local /dev entries or smbfs shares), a colon symbol ':' needs to be prefixed, such as :/dev/sda1.
